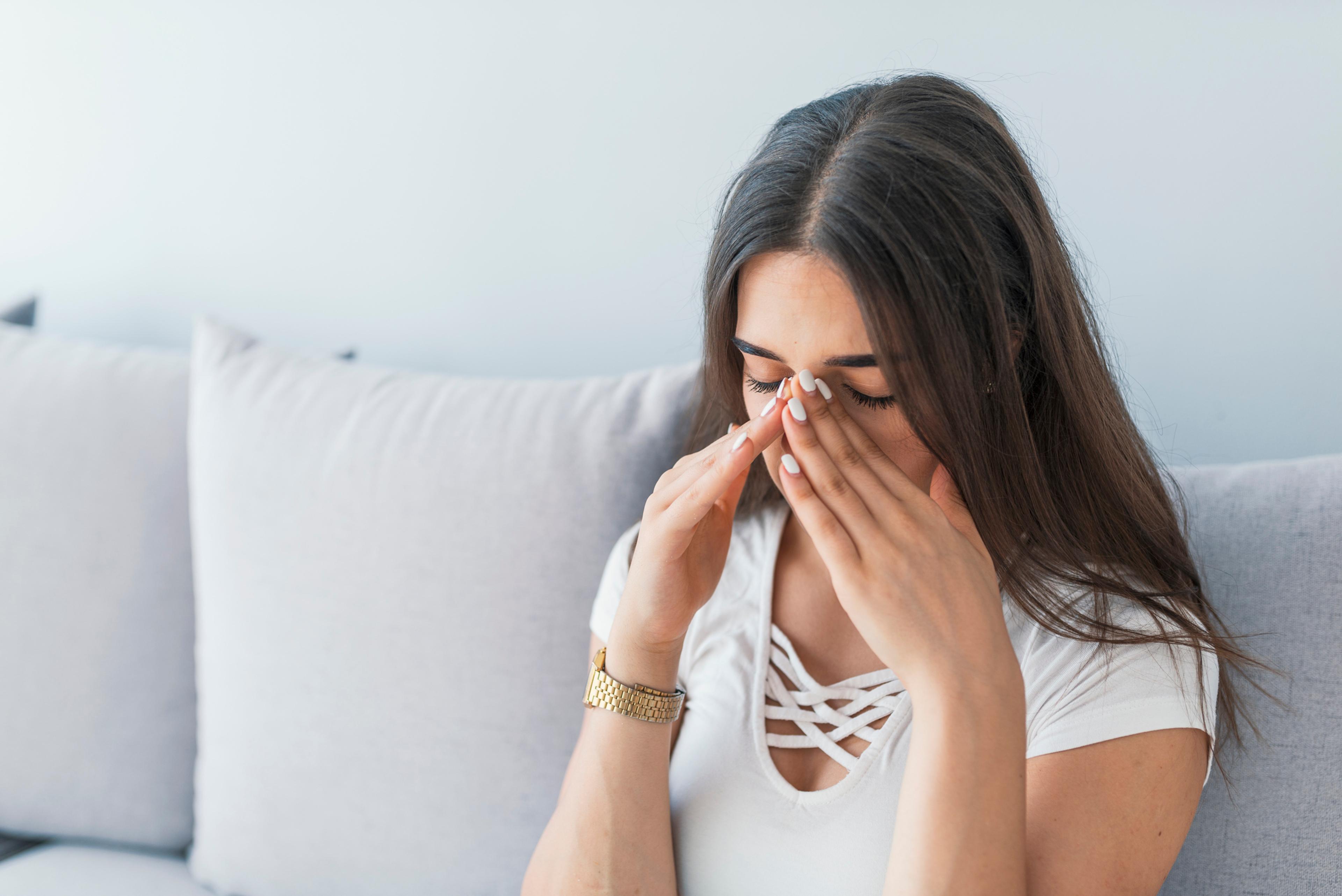
If you've ever had a viral sinus infection, you know how miserable it can be. Pain and pressure develop in the center of your face and it may feel nearly impossible to fully inhale through your nose, which can be stuffy or runny.
Sinus infections don't necessarily overlap with the common cold, though they are associated. You may ask yourself if you can go to work or interact with people in general with a pesky sinus infection. In other words, you may wonder if your sinus infection is contagious.
What is a sinus infection?
Also known as sinusitis, sinus infections occur when fluid builds up in the air-filled pockets of the face. This process inflames the sinuses and promotes germ growth, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Most people have four pairs of sinus cavities in their head. When one or more of these cavities becomes inflamed, the fluid buildup can cause congestion and a runny nose. Common causes of sinus infections include general infections, allergic reactions, deviated septum and nasal polyps.
Upper respiratory infections — such as the cold or flu — are the most common causes of sinus infections, according to Harvard Health. Colds and other respiratory infections can create an environment that allow sinus infections to develop, according to WebMD.
This is because infections can cause tissues in the sinuses to swell and fill with mucus. Additionally, when you blow your nose a lot while sick, this can push bacteria from your nose into your sinuses and worsen the infection.
Are sinus infections contagious?
Sinus infections (acute rhinosinusitis) themselves are not contagious, but the underlying viral upper respiratory infection that commonly precedes and causes most cases of acute sinusitis is contagious.
The American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery and the Infectious Diseases Society of America both note that the majority of acute sinusitis cases are triggered by viral pathogens associated with the common cold, which are readily transmitted from person to person via respiratory droplets.
However, once the viral infection leads to inflammation and obstruction of the sinuses, the subsequent sinusitis — especially if it becomes bacterial — is not directly transmissible.
You don't have to worry about infecting someone with a sinus infection if it was caused by:
- Seasonal allergies.
- Smoking and exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke.
- Structural problems within the sinuses, such as nasal polyps.
- Drugs/medications that weaken the immune system.
- Alcohol
While less common than viral infections, a type of sinus infection called bacterial sinusitis is considered contagious. Bacterial sinus infections often develop as a complication of the aforementioned noninfectious causes, such as viral infections, allergies, or structural issues in the nasal passages.
How to prevent a cold when you feel it coming
If you start to feel a little warm or notice a case of the sniffles creeping up on you, you'll want to hydrate by drinking a lot of water and prioritizing sleep - more so than you even normally would - to nip an oncoming cold in the bud.
Preventing upper respiratory infections can in turn prevent most sinus infections. Here's how the CDC recommends doing that:
- Wash your hands.
- Receive recommended vaccines, such as the flu vaccine and pneumococcal vaccine.
- Avoid close contact with people who have colds or other upper respiratory infections.
- Don't smoke and avoid secondhand smoke.
- Use a clean humidifier to moisten the air at home.
Read on:
- Lyme Disease Cases Up 168% in Michigan Since 2020
- Is There a Link Between Diabetes and Gastroparesis?
- 6 Things Everyone Should Know About the Flu Shot
Photo credit: Getty Images